Preferential site substitution of Eu3+ ions in Ca10(PO4)6Cl2 nanoparticles obtained using a microwave stimulated wet chemistry technique
Abstract
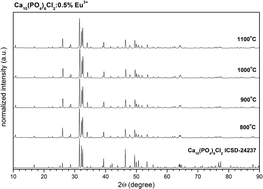
The Eu3+ doped Ca10(PO4)6Cl2 nanocrystalline powders were synthesized using a microwave stimulated technique. Additional post heat treatment in the temperature range 800–1100 °C was applied in order to improve the crystallinity of the final product and eliminate the residual amorphous phase. Detailed structural characterization was performed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman and infrared (IR) spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray fluorescence (EDX). The optical properties of the Ca10(PO4)6Cl2 samples doped with different Eu3+ concentrations (0.5–5 mol%) were determined by measuring excitation, emission spectra and luminescence. TEM images confirmed the nanoscale nature of the final product with a primary particle size of about 60 nm and a hydrodynamic size of 200 nm when the product was dispersed in Milli-Q purified water (MQ) without further stabilization. The analysis of the 5D0 → 7F0 transition points out that for low concentration Ca(II) (A) site is preferentially substituted whereas increase of Eu3+ above 2 mol% results in domination of the Eu3+ cations located at Ca(I) (B) site. Increase of annealing temperature leads to an increase of the 5D0 → 7F0 intensity associated with the Eu3+ at A site. Preferential site substitution can be solved by analysis of the optical properties of the Eu3+ ion. The Judd–Ofelt parameters were calculated using simplified formalisms. The mechanism of concentration quenching process was identified as a dipole–dipole interaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...