Intrinsic bioconjugation for site-specific protein PEGylation at N-terminal serine†
Abstract
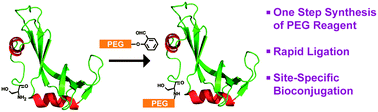
Recently developed chemical ligation protocols were elaborated for rapid N-terminal protein PEGylation. We introduce a PEG-salicylaldehyde ester and demonstrate its site-specific ligation to the N-terminus of the RNase S protein and to the therapeutic polypeptide PTH (1–34).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...