Acetal-linked branched poly(dimethyl-aminoethyl methacrylate) as an acid cleavable gene vector with reduced cytotoxicity†
Abstract
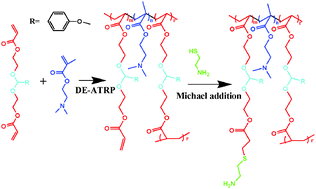
An acid labile branched PDMAEMA/acetal copolymer with amino group was synthesized by the DE-ATRP and followed by Michael addition. The degradation of the polymer was strongly pH-dependent. High nucleic acid transfection efficiency with low cytotoxicity was observed compared to its non-degradable copolymer counterpart.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...