Salt-enabled visual detection of DNA†
Abstract
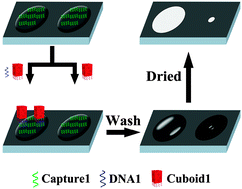
We report herein a label-free, salt-enabled visual detection strategy for DNA, based on the alteration of surface adhesion properties of salt solution, which can translate to the change in the size of the salt residue upon drying, with self-assembled DNA nanostructures. This environmentally friendly array assay protocol enables the achievement of a detection sensitivity comparable to classic colorimetric methods, single-base mismatch differentiation selectivity, multiple-target detection capability, RNA target detection, and a ligase chain reaction-rolling circle amplification implementation format.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...