Boron-doped carbon–iron nanocomposites as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts derived from carbon dioxide†
Abstract
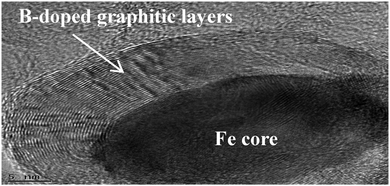
Developing cost-effective oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalysts is pivotal for development of fuel cells. While Fe–N–C catalysts were proposed for ORR, Fe–B–C catalysts have not been explored. This work introduces the B-doped carbon catalysts encapsulating iron cores using CO2 as a carbon source. The Fe–B–C catalysts show enhanced ORR activity and durability due to the iron core within the graphitic layers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...