Oligoamine-tethered low generation polyamidoamine dendrimers as potential nucleic acid carriers†
Abstract
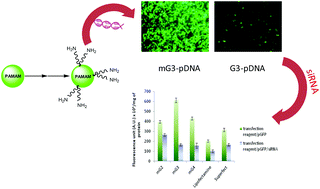
In recent years, dendrimers have emerged as the most widely explored materials for theranostics emphasizing their potential in therapeutic delivery and diagnostics as well as in pharmaceutical technology. Amongst them, PAMAM dendrimers have been extensively studied for their prospects in various biomedical applications due to their defined structures and distinctive features such as monodispersity, uniformity and amenability to functionalization. Here, low generation PAMAM dendrimers (G2–G4) have been modified via Michael addition reaction followed by amidation with an oligoamine linker, tetraethylenepentamine (TEPA). Subsequently, these modified dendrimers were characterized by physicochemical techniques and evaluated for their capability to transfer nucleic acids in vitro. The results displayed significant improvements in the transfection efficiency in both HeLa and A549 cells maintaining higher cell viability. Sequential delivery of GFP-specific siRNA resulted in ∼73% suppression of the target gene. Flow cytometry results revealed that one of the formulations, mG3–pDNA complex, exhibited the highest gene transfection (∼49–68%) outperforming pDNA complexes of native dendrimers and the standard transfection reagent, Superfect (∼32–36%). All these results ensure the potential of the modified dendrimers as effective vectors for future gene delivery applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...