Electrochemical sensing of paracetamol and its simultaneous resolution in the presence of dopamine and folic acid at a multi-walled carbon nanotubes/poly(glycine) composite modified electrode
Abstract
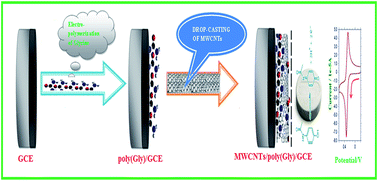
A facile and sensitive nanocomposite sensor was developed based on the electropolymerization of glycine (Gly) onto the surface of a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) using cyclic voltammetry (CV) followed by drop casting multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). The developed nanocomposite sensor (MWCNTs/poly(Gly)/GCE) was characterized using an electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technique. The developed nanocomposite sensor offered high catalytic activity in sensing the paracetamol (PC) individually and simultaneously in the presence of dopamine (DA) and folic acid (FA). The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) were found to be 5 × 10−7 M and 1.7 × 10−6 M respectively with a dynamic range from 5 × 10−7 to 1 × 10−5 M. The fabricated sensor showed good precision and accuracy with a relative standard deviation of 1.28%. The proposed composite sensor was successfully applied towards the determination of PC in human blood serum and pharmaceutical samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...