Highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides using aluminum silicate†
Abstract
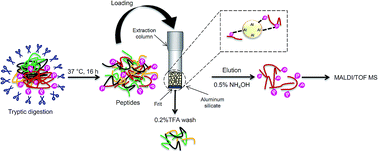
This study presents a novel strategy for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides using aluminium silicate (mullite) powder. Mullite is a nontoxic and inexpensive material and offers excellent performance for the purification of phosphopeptides from complex samples. The selectivity of the method was investigated by matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). The method was validated with tryptic peptides from model proteins, bovine milk and human saliva samples. For sample preparation, the digested samples were loaded on self-assembled extraction columns containing mullite as the sorbent. Non-phosphorylated compounds could be easily removed by several washing steps, while phosphorylated peptides were successfully immobilized on the mullite substrate. In the final step, phosphopeptides were eluted from the extraction column under alkaline conditions. To further assess the enrichment efficiency of the presented method, HeLa cell lysates were spiked with two synthetic phosphopeptides at different ratios. The method showed high selectivity and allowed the detection of phosphopeptides at a ratio of 1 : 1000. In a further study, the performance of the presented approach was compared with that of conventional phosphopeptide enrichment by TiO2 and revealed superior results for aluminium silicate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...