A simple microfluidic electrochemical HPLC detector for quantifying Fenton reactivity from welding fumes
Abstract
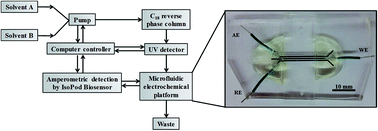
Development and characterization of a simple microfluidic electrochemical flow cell that can be coupled with HPLC to enable dual absorbance/electrochemical detection is described. Coupling absorbance and electrochemical detection increases the information that can be gathered from a single injection, but a second (typically expensive) detection system is required. Here, an inexpensive, customizable microfluidic electrochemical detector is coupled in series with a commercial HPLC/UV system. The microfluidic device is made from poly(dimethylsiloxane) and contains carbon paste electrodes. To demonstrate the utility of this dual-detection system, the reaction products of the radical scavenging agent salicylic acid and hydroxyl radical generated by Fenton chemistry were analyzed. The dual-detection system was used to quantify 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid, and catechol produced by the addition of H2O2 to filter samples of welding fumes. Measurement recovery was high, with percent recoveries between 97–102%, 92–103%, and 95–103% for 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid, and catechol, respectively, for control samples. The methods described in this work are simple, reliable, and can inexpensively couple electrochemical detection to HPLC-UV systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...