The quantification of human chorionic gonadotropin by two isotope dilution mass spectrometry methods†
Abstract
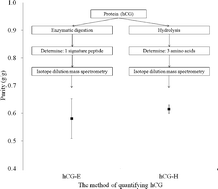
Two isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) methods were established and compared for absolute quantification of the mass fraction of an important clinical diagnostic marker, i.e. human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), by employing hydrolysis and enzymatic digestion. In the first method, after hydrolysis of the protein, amino acids were separated by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and then detected by tandem mass spectrometry (MS) with multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) for phenylalanine, proline, valine and the internal standards (13C9-phenylalanine, 13C5-proline and 13C5-valine). In the second method, after enzyme digestion, the signature peptide (VLQGVLPALPQVVCNYR, m/z = 964 → 1036) and the internal standard (d10-VLQGVL*PALPQVVCNYR, m/z = 970 → 1317) were separated by HPLC, and then detected by MS with MRM. By optimizing the key factors of hydrolysis and enzymatic digestion, the mass fractions of hCG detected by these two methods are consistent. The mass fraction of hCG by hydrolysis is 0.6150 g g−1 (expanded uncertainty = 0.016 g g−1, k = 2), the mass fraction of hCG by enzyme digestion is 0.5810 g g−1 (expanded uncertainty = 0.072 g g−1, k = 2), and the weighted average mass fraction is 0.6126 g g−1 (expanded uncertainty = 0.016 g g−1, k = 2). This study would benefit the absolute quantification of clinical marker proteins, and underpin the development of relative certified reference materials of clinical diagnostic markers to ensure the accuracy, comparability and traceability of medical laboratory testing.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...