Development of a methodology for accurate quantitation of alkylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in petroleum and oil contaminated environmental samples
Abstract
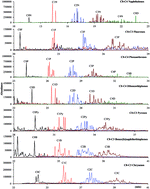
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are compounds of concern because most of these compounds are toxic, carcinogenic, or mutagenic and are relatively persistent in the environment. Reliable quantitative information of PAHs is important to evaluate the acute and chronic harmful effects of PAHs on the ecosystem. Crude oils and refined petroleum products contain many highly abundant PAHs and heterocyclic PAHs, in particular the alkylated homologues of naphthalene, phenanthrene, dibenzothiophene, fluorene and chrysene (APAH). The alkylated PAH homologues usually occur in significantly higher concentrations than their corresponding unsubstituted parent PAHs. Petrogenic alkylated PAHs generally consist of large numbers of isomers. Unlike those individual unsusbstituted PAHs, most of the APAH isomers are not commercially available. Therefore, historically, the target APAHs are generally quantified using the relative response factors (RRFs) obtained from their respective unsubstituted parent PAH compounds, this inevitably results in the quantitative results of APAH being significantly underestimated. In order to improve the accuracy of the measurement of PAHs and their alkylated homologues in oil and oil related samples, this study measured and compared the response factors of a large number of alkylated PAHs relative to the internal standards in gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis, with the goal of developing a more accurate quantitative methodology for the determination of oil APAHs, and eventually leading to a standardized methodology of quantitative APAH analysis. The PAHs in different oils and related environmental samples collected from oil impacted areas were determined using this GC-MS methodology. Furthermore, the influence of the measurement methodology on the diagnostic ratios of target PAHs was also assessed in this work.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...