Hollow-fiber membrane tube embedded with a molecularly imprinted monolithic bar for the microextraction of triazine pesticides
Abstract
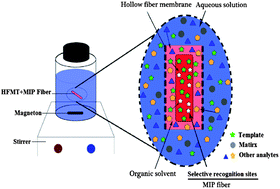
A molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) monolith was initially prepared in a silica capillary mold by microwave irradiation. After the silica wall was etched away after polymerization, the resulting monolithic bar was embedded in a porous hollow fiber membrane tube (HFMT), in which a thin supported liquid membrane (SLM) was formed in the pores and an acceptor solution was filled in its lumen. It can be used to overcome the common water-compatibility problem in the MIP application by the developed hollow fiber–liquid–solid microextraction (HFLSME) system. The main factors affecting the selective extraction including extraction and desorption time, extraction solvent in the hollow fiber (HF) lumen, off-line desorption solvent, stirring rate and pH of the sample solution were investigated for HFLSME procedures in detail. Selectivity was also evaluated using the atrazine template molecule, its analogues and non-analogue. The extraction amount for each structurally-related pesticide including atrazine, 2-amino-4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazine, terbutylazine and ametryn was obtained about 10 times using atrazine-imprinted hollow fiber than that using non-imprinted hollow fiber, whilst no obvious difference was found for its non-analogues of metribuzin. The resulted hollow fibers were successfully applied to detect atrazine and its analogues in lake water coupled to high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and resulted in recoveries in the range of 72.8–113.2%, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...