Evaluation of agglutination strength by a flow-induced cell movement assay based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technique†
Abstract
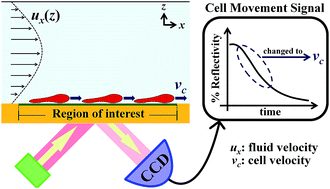
A flow-induced cell movement assay combined with a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technique was developed to quantify the agglutination strength, derived from the standard tube-agglutination test. Red blood cells (RBCs), based on the ABO blood group system, were specifically captured by anti-A and/or anti-B antibodies immobilized on a sensor surface. The agglutination strength corresponds to the amount of antigen–antibody interactions or the strength of RBC adhesion. Under a shear flow, the adherent RBCs were forced to move out of the region of interest with different average cell velocities (vc) depending upon the adhesion strength and wall shear stress (WSS). That is, a higher adhesion strength (higher agglutination strength) or lower WSS represents a lower vc or vice versa. In this work, the agglutination strength was derived from the vc that was calculated from the time derivative of the relative SPR signal by using a simple model of cell movement response, whose validity was verified. The vc values of different samples were correlated with their agglutination strengths at a given WSS and antibody surface density. The vc decreased as the agglutination strength increased, which can be considered as a linear regression. The coefficient of variation of the calculated vc decreased to 0.1 as vc increased to 30 μm min−1. The sensitivity of this assay can be controlled by optimizing the antibody surface density or the WSS. This assay has the capability to resolve the antigen density of A1 and B RBCs from that of A1B RBCs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...