The multivariate detection limit for Mycoplasma pneumoniae as determined by nanorod array-surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and comparison with limit of detection by qPCR†
Abstract
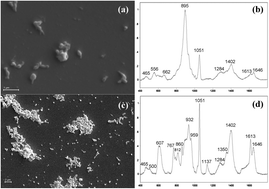
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a cell wall-less bacterial pathogen of the human respiratory tract that accounts for up to 20% of community-acquired pneumonia. At present, the standard for detection and genotyping is quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), which can exhibit excellent sensitivity but lacks standardization and has limited practicality for widespread, point-of-care use. We previously described a Ag nanorod array-surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (NA-SERS) biosensing platform capable of detecting M. pneumoniae in simulated and true clinical throat swab samples with statistically significant specificity and sensitivity. We report here that differences in sample preparation influence the integrity of mycoplasma cells for NA-SERS analysis, which in turn impacts the resulting spectra. We have established a multivariate detection limit (MDL) using NA-SERS for M. pneumoniae intact-cell sample preparations. Using an adaptation of International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC)-recommended methods for analyzing multivariate data sets, we found that qPCR had roughly 10× better detection limits than NA-SERS when expressed in CFU ml−1 and DNA concentration (fg). However, the NA-SERS MDL for intact M. pneumoniae was 5.3 ± 1.0 genome equivalents (cells per μl). By comparison, qPCR of a parallel set of samples yielded a limit of detection of 2.5 ± 0.25 cells per μl. Therefore, for certain standard metrics NA-SERS provides a multivariate detection limit for M. pneumoniae that is essentially identical to that determined via qPCR.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...