Electrochemical detection of glycan and protein epitopes of glycoproteins in serum
Abstract
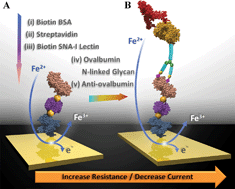
Aberrant protein glycosylation is associated with a range of pathological conditions including cancer and possesses diagnostic importance. Translation of glycoprotein biomarkers will be facilitated by the development of a rapid and sensitive analytical platform that simultaneously interrogates both the glycan and protein epitopes of glycoproteins in body fluids such as serum or saliva. To this end, we developed an electrochemical biosensor based on the immobilization of a lectin on the gold electrode surface to recognize/capture a target glycan epitope conjugated to glycoproteins, followed by detection of the protein epitope using a target protein-specific antibody. Electrochemical signals are generated by label-free voltammetric or impedimetric interrogation of a ferro/ferricyanide redox couple (e.g. [Fe(CN)6]3−/4−) on the sensing surface, where the change in voltammetric current or interfacial electron transfer resistance was measured. The detection system was demonstrated using the model glycoprotein chicken ovalbumin with Sambucus nigra agglutinin type I (SNA lectin), and exhibits femtomolar sensitivity in the background of diluted human serum. The results obtained in this proof-of-concept study demonstrate the possibility of using electrochemical detection for developing cheap point-of-care diagnostics with high specificity and sensitivity for blood glycoprotein biomarkers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...