Biologically triggered liberation of sub-micron particles from alginate microcapsules†
Abstract
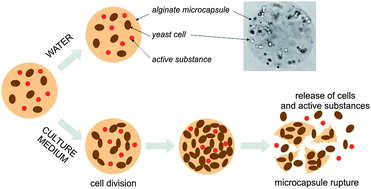
A new method for triggering the burst liberation of encapsulated sub-micron particles from carrier particles using embedded microorganisms has been developed. Triggering mechanisms such as those based on chemical, light, thermal, or magnetic stimuli are known, but man-made particles are not yet able to replicate the concept of “dormancy” found in biological systems in the form of spores or seeds that survive in an inactive state and start to grow only once favourable environmental conditions are encountered. An engineered particle system that mimics this property by embedding viable yeast cells into synthetically made alginate microcapsules is reported in the present work. Cell growth and division is used as a triggering mechanism for stimuli-responsive release of the encapsulated content. The hybrid living/artificial capsules were formed by an inkjet printing process and the mechanism of biologically triggered release was shown using fluorescently labelled liposomes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...