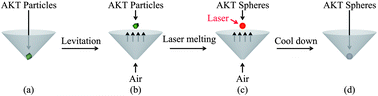
Bioceramic spheres have been widely studied for bone/dental filler materials. Conventional methods, such as alginate cross-linking, microemulsion and spray drying, have distinct disadvantages for preparing pure bioceramic spheres with controllable size, bioactivity and degradation. In this study, a containerless processing method, for the first time, was applied to prepare bioceramic spheres for potential bone/dental filling applications. Akermanite (Ca2MgSi2O7, AKT) glass spheres were firstly prepared by a unique containerless processing method. Then, the as-prepared AKT glass spheres were heat-treated at varied temperatures. Furthermore, the effect of heat treatment on the phase transition, surface microstructure, apatite mineralization and ionic dissolution production of AKT spheres has been systematically studied. The interaction of MC3T3 cells with AKT spheres was further studied by investigating cell attachment, proliferation and alkaline phosphate (ALP) activity. The results show that containerless processing is a quite effective method to prepare homogeneous AKT glass spheres with controllable size. Heat-treatment promotes the phase transition from amorphous, semi-crystalline to fully crystalline AKT spheres. Thus, AKT spheres with controllable crystallinity were successfully prepared by combining containerless processing and heat treatment. The as-prepared AKT glass spheres induced apatite mineralization after soaking in simulated body fluids (SBF) for 7 days; however, AKT spheres treated at 800 °C suppressed apatite mineralization in SBF. Interestingly, AKT spheres treated at 1000 or 1350 °C had distinct apatite mineralization, indicating that the bioactivity of the AKT spheres can be regulated by modulating the heat-treatment-induced crystallinity. Further study has shown that the ionic dissolution production of the containerless-processed AKT spheres can be tailored by controlling the heat-treatment temperatures. The prepared crystalline AKT spheres supported the attachment, spreading, growth and early differentiation of MC3T3 cells, and significantly stimulated the proliferation of MC3T3. Therefore, the containerless-processed AKT spheres may be a unique bone/dental filler material due to their homogeneous structure, controllable size, bioactivity and ionic degradation, as well as their excellent cytocompatibility.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...