Mesoscopic magnetic iron oxide spheres for high performance Li-ion battery anode: a new pulsed laser induced reactive micro-bubble synthesis process†
Abstract
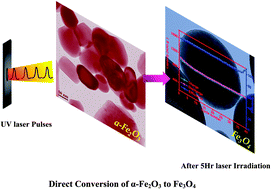
Spherical particles of iron oxide (mainly Fe3O4 with a small contribution of α-Fe2O3) having a size of about ∼200 nm are synthesized from bulk commercial α-Fe2O3 powder by a pulsed excimer laser irradiation technique in solution phase. The dispersed α-Fe2O3 powder is subjected to a pulsed excimer laser (248 nm) irradiation at an energy density of ∼214 mJ cm−2 and pulse repetition rate of 10 Hz for 5 h under constant stirring in the presence of aqueous ammonia. It has been observed that the α-Fe2O3 particles get gradually converted into Fe3O4, which can be visualized from the change in the color of the solution from red to dark red, and then finally to a black colored solution. The phase conversion from α-Fe2O3 to Fe3O4 has also been confirmed by various characterizations, such as Raman and Mössbauer spectra. From the Mössbauer spectra at the end of 5 h laser irradiation 87% of Fe3O4 was observed. The detailed mechanism of the formation of these particles has been investigated. The performance of these particles was verified for use as anode materials in Li ion batteries. The iron oxide particles show a capacity of 1100 mA h g−1 at a current density of 100 mA g−1. This capacity is highly stable up to 40 cycles without any significant capacity fading. A coulombic efficiency of 97% has been achieved with high stability and reversibility.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...