A two-electron mechanism of lithium insertion into layered α-MoO3: a DFT and DFT+U study
Abstract
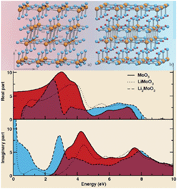
We study the changes in electrodynamic responses due to Li insertion into layered α-MoO3. We compute electronic and dielectric properties, including the optical conductivity response of pure and lithiated

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...