Magnetically induced phase condensation in an aqueous dispersion of magnetic nanogels†
Abstract
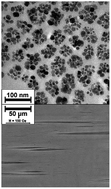
The applicability of aqueous magnetic colloids depends on their colloidal stability under the influence of various factors like external magnetic field and temperature. The magnetically induced phase condensation of magnetic colloids leads to the formation of spindle-like condensed phase drops of highly packed magnetic colloidal particles. The condensed phase drops are aligned parallel to the external magnetic field and may grow up to several microns thickness and tens or even hundreds of microns length. Thus, the magnetically induced phase condensation could be an advantage in magnetic separation applications, whereas in magnetic

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...