Site-specific inter-strand cross-links of DNA duplexes†
Abstract
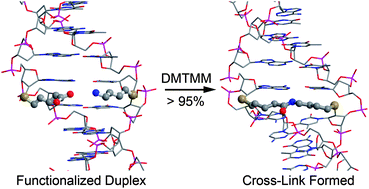
We report the development of technology that allows inter-strand coupling across various positions within one turn of DNA. Four 2′-modified nucleotides were synthesized as protected phosphoramidites and incorporated into DNA oligonucleotides. The modified nucleotides contain either 5-atom or 16-atom linker components, with either amine or carboxylic acid functional groups at their termini, forming 10 or 32 atom (11 or 33 bond) linkages. Chemical coupling of the amine and carboxylate groups in designed strands resulted in the formation of an amide bond. Coupling efficiency as a function of trajectory distance between the individual linker components was examined. For those nucleotides capable of forming inter-strand cross-links (ICLs), coupling yields were found to depend on temperature, distance, and linker length, enabling several approaches that can control regioselective linkage. In the most favorable cases, the coupling yields are quantitative. Spectroscopic measurements of strands that were chemically cross-linked indicate that the global structure of the DNA duplex does not appear to be distorted from the B form after coupling. Thermal denaturing profiles of those strands were shifted to somewhat higher temperatures than those of their respective control duplexes. Thus, the robust amide ICLs formed by this approach are site-specific, do not destabilize the rest of the duplex, and only minimally perturb the secondary structure.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...