A highly sensitive and selective resonance Rayleigh scattering method for bisphenol A detection based on the aptamer–nanogold catalysis of the HAuCl4–vitamin C particle reaction†
Abstract
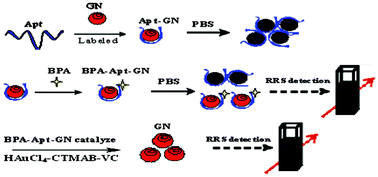
Based on the catalytic effect of the bisphenol A aptamer-modified

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...