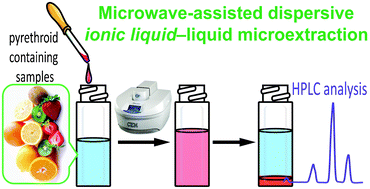
In the present study, we have developed a novel dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) based on microwave-assisted DLLME (MADLLME) using ionic liquids for the separation of environmentally-relevant pyrethroid pesticides from various aqueous milieux. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was employed for the detection and quantitative tracking of the pesticides. Six different ILs were preliminarily tested as extraction solvents against four representative model pyrethroids. The optimization of the current method was derived by consideration of the dispersal solvent, ionic liquid choice, extraction container material, aqueous-phase pH, and microwave conditions (particularly, the applied power and irradiation time). Optimal results were achieved using methanol as a dispersal solvent with trioctylmethylammonium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ([N8881][Tf2N]) as the extraction solvent at a microwave power of 200 W for 60 s. A number of spiked food samples (e.g., honey, milk, assorted fruits) were also tested using MADLLME, with excellent recoveries achieved from these complex matrices as compared to DLLME alone.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...