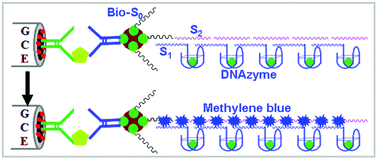
This work reports a new electrochemical immunoassay protocol with signal amplification for the sensitive detection of a biomarker (carcinoembryonic antigen, CEA, used in this case) by coupling hemin/G-quadruplex-constructed DNAzyme concatamer with the biotin-avidin amplification system. Initially, polyclonal rabbit anti-human CEA antibody (pAb1) was immobilized onto a gold nanoparticle-modified glassy carbon electrode, which was used for the capture of target CEA, and biotin-labeled mouse anti-human monoclonal CEA antibody (bio-mAb2) was then used as a secondary antibody for the formation of the sandwiched immunocomplex in the presence of target CEA on the pAb1-modified electrode. The carried biotin could react with streptavidin and a biotin-labeled initiator strand (S0) in sequence. Two auxiliary DNA strands (S1 and S2) were designed for the concatamer reaction with the S0. The DNA initiator stand (S0) could propagate a chain reaction of hybridization events between alternating S1 and S2 to form a nicked double-helix. Upon addition of hemin, the hemin-binding aptamers can be bound to form the hemin/G-quadruplex-based DNAzymes on the S1 probe. Meanwhile, the formed double-helix DNA polymers could also cause the numerous intercalation of electroactive methylene blue. During the electrochemical measurements, the DNAzymes could catalyze the reduction of H2O2 in a detection solution with the aid of the intercalated methylene blue. Under the optimal conditions, the electrochemical immunosensor exhibited a dynamic working range of 1.0 pg mL−1–50 ng mL−1 toward CEA standards with a detection limit of 0.5 pg mL−1. The reproducibility and selectivity of the developed immunoassay were acceptable (CV <10%). In addition, 6 spiked CEA samples with various concentrations were assayed by using the developed immunoassay, and the recovery was 92–120%.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...