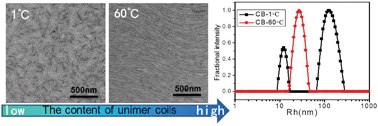
It was found that free poly(3,3′′′-didodecylquaterthiophene) (PQT-12) unimer coils in solution had a significant effect on the formation of aligned fibrils in thin films. Long and parallel aligned nano-fibrils formed easily when more unimer coils existed in solution. In contrast, small rod-like crystals with a random orientation would form when less unimer coils existed in solution. The content of unimer coils in solution was increased by the methods such as choosing proper solvents, elevating the temperature and filtering aggregates in solution, etc. For example, the proportion of PQT-12 unimer coils in chlorobenzene increased from 19.9% to 100% when the temperature was raised from 1 °C to 60 °C. During the evaporation of solvents, the conformation of the unimer coils in solution transformed from coils to extended chains firstly, and then ordered aggregates formed. The ordered aggregates assembled into nano-fibrils via π–π interaction. The rest of ordered aggregates in solution adhered to the boundaries of the nano-fibrils and grew along the boundaries of nano-fibrils to form parallel fibers. The parallel aligned fibers preferred an edge-on orientation without chain-folding due to the high backbone rigidity of PQT-12.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...