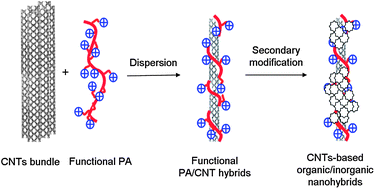
Functional polyacetylenes (PAs) have attracted great interest and a series of tutorial reviews dealing with the recent progress in the related fields can be found in the literature. The investigation of the hybrids of functional PAs and inorganic nanostructures is a newly asserted and developing area. In this review, we summarise the related works on the hybrids of functional PAs and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) reported in the last decade. The effects of the structural parameters such as the polymer mainchain, functional pendants and the linker between them on the solvating power towards CNTs are explored step-by-step. Concerning the mechanisms of dispersing CNTs into solvents, a novel factor, or donor–acceptor interaction, has been singled out, thus providing a novel concept to design functional polymers for the fabrication of CNT-based processable hybrids. The strong solvating power of properly designed functional PAs facilitates the non-harmful surface functionalization of CNTs and permits using the hybrids of PAs/CNTs as templates to derive multi-component nanocomposites. Different nanostructures including Ag nanoparticles, ZnO nanocrystallites, CdS nanorods and γ-Fe3O4 nanoparticles are successfully incorporated into the functional PAs/CNTs hybrid systems, which show efficient charge transfer, charge carrier transport, enhanced solvatochromism, and superparamagnetic properties. Rationally functionalized PAs demonstrate good biocompatibility and their hybrids with CNTs can be used as active additives to reinforce the bending strength and modulus of chitosan rods. Finally, a brief outlook of the promising directions in this promising research area is contributed.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...