Use of a switchable hydrophobic associative polymer to create an aqueous solution of CO2-switchable viscosity†
Abstract
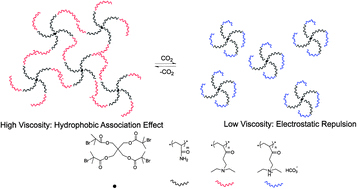
We synthesized a new four-armed star-like hydrophobic associative polymer containing polyacrylamide core sections and poly(N,N-diethylaminoethyl methacrylate) CO2-switchable chain ends. The aqueous solution of the polymer is viscous due to formation of a network structure in the absence of CO2 but nonviscous in its presence. The viscosity also is enhanced with increasing concentration of NaCl.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...