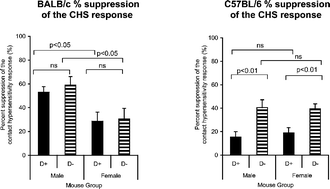
Ultraviolet B (UVB) irradiation of the skin has the benefit of causing the local production of previtamin D3 but also results in cutaneous DNA damage and suppression of the skin immune system (SIS). Strains of mice differ in their ability to be suppressed by UVB irradiation: BALB/c mice are considered “resistant” and C57BL/6 “sensitive”. This study evaluated whether vitamin D-replete (D+) and deficient (D−) BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice differed in their cutaneous response to UVB irradiation. Immunosuppression was assessed by measuring the contact hypersensitivity (CHS) response, DNA damage and repair determined by counting thymine dimer positive keratinocyte nuclei, and cutaneous inflammation and epidermal hyperplasia evaluated by light microscopy. The suppression in the CHS response induced by the UVB irradiation was reduced in the D+ C57BL/6 mice compared with the D− C57BL/6 mice. Similarly there was a reduction in DNA damage and promotion of its repair in the D+ C57BL/6 mice compared with the D− C57BL/6 mice. A reduction in inflammation in female D+ C57BL/6 mice compared with D− C57BL/6 females also occurred. In contrast, the suppression in the CHS response, DNA damage and its repair, and inflammation induced by UVB irradiation were similar in the D+ and D− BALB/c mice. These results indicate that dietary vitamin D3 can reduce UVB-induced suppression of the CHS response depending on the genetic background of the mice, an effect that may relate to the reduction in DNA damage and an increase in its rate of repair.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...