Inhibition studies on Mycobacterium tuberculosis N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GlmU)†
Abstract
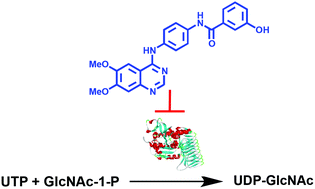
Peptidoglycan is an essential component of the cell wall of bacteria, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, that provides structural strength and rigidity to enable internal osmotic pressure to be withstood. The first committed step in the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan involves the formation of uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) from uridine triphosphate (UTP) and GlcNAc-1-phosphate. This reaction is catalysed by N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GlmU), a bifunctional enzyme with two independent active sites that possess acetyltransferase and uridyltransferase activities. Herein, we report the first inhibition study targeted against the uridyltransferase activity of M. tuberculosis GlmU. A number of potential inhibitors were initially prepared leading to the discovery of active aminoquinazoline-based compounds. The most potent inhibitor in this series exhibited an IC50 of 74 μM against GlmU uridyltransferase activity and serves as a promising starting point for the discovery of more potent inhibitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...