Photoswitchable DNA-binding properties of a photochromic spirooxazine derivative†
Abstract
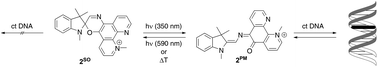
An N-methylphenanthrolinium-annelated spirooxazine derivative 2SO whose DNA-intercalating properties are reversibly changed by a photochromic reaction was prepared. Upon irradiation at 350 nm the spirooxazine is transformed to the corresponding photomerocyanine 2PM that binds to DNA. After irradiation with visible light the spirooxazine 2SO, which exhibits no significant DNA-binding properties, is regained. The association of 2PM with DNA was examined by CD and absorption spectroscopy, fluorescent intercalator displacement and viscometric titration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...