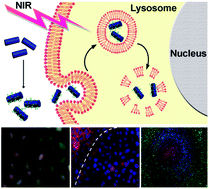
Recently, photothermal ablation therapy (PTA) employing near-infrared radiation (NIR) has been extensively investigated as an emerging modality for cancer management. However, the clinical translation of this promising approach is limited by the lack of PTA agents with broad NIR absorption, low cost and high photothermal conversion efficiency. Herein, we have developed PEGylated homogeneous CsxWO3 nanorods (a mean size ∼69.3 nm × 12.8 nm) with broad photo-absorption (780–2500 nm) as a novel NIR absorbent for PTA treatment of human cancer. The prepared CsxWO3 nanocrystals displayed strong near-infrared optical absorption with a high molar extinction coefficient (e.g. 4.8 × 1010 M−1 cm−1 at 980 nm), thus generated significant amounts of heat upon excitation with near-infrared light. The PTA study in two human carcinoma cell lines (i.e. A549 lung cancer cells and HeLa ovarian cancer cells) demonstrated that CsxWO3 nanorods can efficiently cause cell death via hyperthermia induced lysosome destruction, cytoskeleton protein degradation, DNA damage and thereafter cellular necrosis or apoptosis. Our study also confirmed the migration of healthy cells migrated from unirradiated areas to dead cell cycle, which is essential for tissue reconstruction and wound healing after photodestruction of tumor tissue. The prompted results reported in the current study imply the promising potential of CsxWO3 nanorods for application in PTA cancer therapy.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...