Synthesis of nanostructured materials by using metal-cyanide coordination polymers and their lithium storage properties†
Abstract
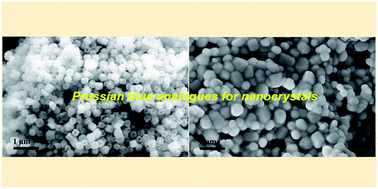
Herein, we demonstrate a novel and simple two-step process for preparing LiCoO2 nanocrystals by using a Prussian blue analogue Co3[Co(CN)6]2 as a precursor. The resultant LiCoO2 nanoparticles possess single crystalline nature and good uniformity with an average size of ca. 360 nm. The unique nanostructure of LiCoO2 provides relatively shorter Li+ diffusion pathways, thus facilitating the fast kinetics of electrochemical reactions. As a consequence, high reversible capacity, excellent cycling stability and rate capability are achieved with these nanocrystals as cathodes for lithium storage. The LiCoO2 nanocrystals deliver specific capacities of 154.5, 135.8, 119, and 100.3 mA h g−1 at 0.2, 0.4, 1, and 2 C rates, respectively. Even at a high current density of 4 C, a reversible capacity of 87 mA h g−1 could be maintained. Importantly, a capacity retention of 83.4% after 100 cycles is achieved at a constant discharge rate of 1 C. Furthermore, owing to facile control of the morphology and size of Prussian blue analogues by varying process parameters, as well as the tailored design of multi-component metal–cyanide hybrid coordination polymers, with which we have successfully prepared porous Fe2O3@NixCo3−xO4 nanocubes, one of the potential anode materials for lithium-ion batteries, such a simple and scalable approach could also be applied to the synthesis of other nanomaterials for energy storage devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...