Synergetic regulatory networks mediated by oncogene-driven microRNAs and transcription factors in serous ovarian cancer†
Abstract
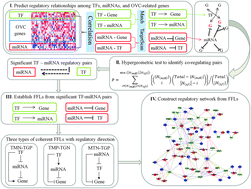
Although high-grade serous ovarian cancer (OVC) is the most lethal gynecologic malignancy in women, little is known about the regulatory mechanisms in the cellular processes that lead to this cancer. Recently, accumulated lines of evidence have shown that the interplay between transcription factors (TFs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) is critical in cellular regulation during tumorigenesis. A comprehensive investigation of TFs and miRNAs, and their target genes, may provide a deeper understanding of the regulatory mechanisms in the pathology of OVC. In this study, we have integrated three complementary algorithms into a framework, aiming to infer the regulation by miRNAs and TFs in conjunction with gene expression profiles. We demonstrated the utility of our framework by inferring 67 OVC-specific regulatory feed-forward loops (FFL) initiated by miRNAs or TFs in high-grade serous OVC. By analyzing these regulatory behaviors, we found that all the 67 FFLs are consistent in their regulatory effects on genes that are jointly targeted by miRNAs and TFs. Remarkably, we unveiled an unbalanced distribution of FFLs with different oncogenic effects. In total, 31 of the 67 coherent FFLs were mainly initiated by oncogenes. On the contrary, only 4 of the FFLs were initiated by tumor suppressor genes. These overwhelmingly observed oncogenic genes were further detected in a sub-network with 32 FFLs centered by miRNA let-7b and TF TCF7L1 to regulate cell differentiation. Closer inspection of 32 FFLs revealed that 75% of the miRNAs reportedly play functional roles in cell differentiation, especially when enriched in epithelial–mesenchymal transitions. This study provides a comprehensive pathophysiological overview of recurring coherent circuits in OVC that are co-regulated by miRNAs and TFs. The prevalence of oncogenic coherent FFLs in serous OVC suggests that oncogene-driven regulatory motifs could cooperatively act upon critical cellular processes such as cell differentiation in a highly efficient and consistent manner.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...