High-throughput ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry characterization of metabolites guided by a bioinformatics program†
Abstract
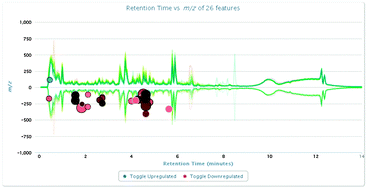
Metabolite profiling in biomarker discovery research requires new data preprocessing approaches to correlate specific metabolites to their biological origin. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics often results in the observation of hundreds to thousands of features that are differentially regulated in biosamples. Extracting biomedical information from large metabolomic datasets by multivariate data analysis is of considerable complexity. Therefore, more efficient and optimized metabolomics data processing technologies are needed to improve MS applications in biomarker discovery. Here we use a sensitive ultra-performance LC-ESI/quadrupole-TOF high-definition mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS) approach, in negative ion mode, to characterize metabolites. XCMS online analysis was used which incorporates novel nonlinear retention time alignment, matched filtration, peak detection, and peak matching. XCMS software can facilitate prioritization of the data and greatly increases the probability of identifying metabolites causally related to the phenotype of interest. 26 urinary differential metabolites contributing to the complete separation of HCC patients from matched healthy controls were identified involving the key metabolic pathways including tyrosine metabolism, glutathione metabolism, phenylalanine metabolism, ascorbate and aldarate metabolism, and arginine and proline metabolism. It demonstrates that high-throughput UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS metabonomics combined with the proposed bioinformatic approach (based on XCMS) are pivotal to elucidate the developing biomarkers and physiological mechanism of disease in a clinical setting.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...