Quantitative global phosphoproteomics of human umbilical vein endothelial cells after activation of the Rap signaling pathway†
Abstract
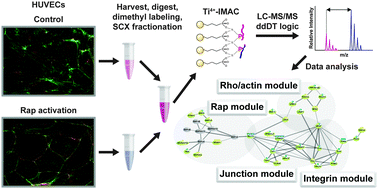
The small GTPase Rap1 is required for proper cell–cell junction formation and also plays a key role in mediating cAMP-induced tightening of adherens junctions and subsequent increased barrier function of endothelial cells. To further study how Rap1 controls barrier function, we performed quantitative global phosphoproteomics in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) prior to and after Rap1 activation by the Epac-selective cAMP analog 8-pCPT-2′-O-Me-cAMP-AM (007-AM). Tryptic digests were labeled using stable isotope dimethyl labeling, enriched with phosphopeptides by strong cation exchange (SCX), followed by titanium(IV) immobilized metal affinity chromatography (Ti4+-IMAC) and analyzed by high resolution mass spectrometry. We identified 19 859 unique phosphopeptides containing 17 278 unique phosphosites on 4594 phosphoproteins, providing the largest HUVEC phosphoproteome to date. Of all identified phosphosites, 220 (∼1%) were more than 1.5-fold up- or downregulated upon Rap activation, in two independent experiments. Compatible with the function of Rap1, these alterations were found predominantly in proteins regulating the actin cytoskeleton, cell–cell junctions and cell adhesion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...