Genome-wide transcriptional responses of Escherichia coli to glyphosate, a potent inhibitor of the shikimate pathway enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase†
Abstract
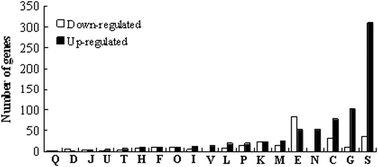
The shikimate pathway enzymes offer attractive targets for the development of antimetabolites. Glyphosate is an effective antimetabolite that inhibits 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase in the shikimate pathway, thereby resulting in a shortage of the chorismate-derived essential aromatic amino acids. However, little is known about the genome-wide transcriptional responses of bacteria to glyphosate shock. In the current study, a transcriptome analysis of Escherichia coli (E. coli) exposed to glyphosate identified the differential expression of 1040 genes, which represent 23.2% of the genome. The differentially expressed genes are primarily involved in amino acid metabolism, cell motility, and central carbon metabolism, indicating that the impact of glyphosate on the shikimate pathway also extends to other metabolic pathways. Expectedly, almost all genes encoding the proteins for the shikimate and specific aromatic amino acid pathways were downregulated after the addition of glyphosate. Furthermore, the expression of many energy- and metabolism-related genes was repressed. In contrast, glyphosate treatment induced the coordinated upregulation of at least 50 genes related to cell motility and chemotaxis. The reverse transcription-quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) data showed that the expression profiles of selected genes from the referred pathways were found to be consistent with the microarray data. The results suggest that the presence of glyphosate during growth induces metabolic starvation, an energy drain and other non-target effects.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...