Electrofluidic pressure sensor embedded microfluidic device: a study of endothelial cells under hydrostatic pressure and shear stress combinations
Abstract
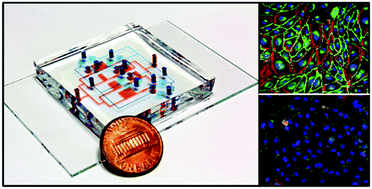
Various microfluidic cell culture devices have been developed for in vitro cell studies because of their capabilities to reconstitute in vivo microenvironments. However, controlling flows in microfluidic devices is not straightforward due to the wide varieties of fluidic properties of biological samples. Currently, flow observations mainly depend on optical imaging and macro scale transducers, which usually require sophisticated instrumentation and are difficult to scale up. Without real time monitoring, the control of flows can only rely on theoretical calculations and numerical simulations. Consequently, these devices have difficulty in being broadly exploited in biological research. This paper reports a microfluidic device with embedded pressure sensors constructed using electrofluidic circuits, which are electrical circuits built by fluidic channels filled with

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...