Comparison of inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry, energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in the elemental analysis of agricultural soils†
Abstract
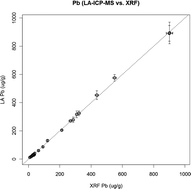
A silica sol–gel technique was applied to the preparation of pellets of agricultural soils for determination of trace elements by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). For the purpose of evaluation of feasibility of the LA-ICP-MS technique for quantitative determination, elemental contents in twenty two spiked archive agricultural soils and three CRMs (GBW07405, GBW07406, and GBW07407) were determined by independent analytical techniques, namely by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry with pneumatic nebulization (PN-ICP-OES) after total decomposition with a mixture of acids, and by energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (ED-XRF) spectrometry analysis of pellets prepared with a wax binder. Ablation was carried out with a Nd:YAG laser at 213 nm. Possible matrix interferences associated with ablation of the multiphase soil material were anticipated and therefore, the sequential extraction procedure was employed for fractionation analysis to determine elemental concentrations, in particular soil constituents, for explaining potential deviations of LA-ICP-MS analyses. Methods were compared based on the determination of ordinarily monitored trace elements Cu, Cr, Ni, Pb and Zn in archive soils and certified reference materials. The PN-ICP-OES, ED-XRF and LA-ICP-MS methods were compared by means of linear regression analysis to search for a possible systematic proportional or constant error. Besides the ordinary least-squares linear regression method, also weighted least squares, orthogonal, Deming, maximum likelihood and Passing–Bablok regressions were employed. The Bland–Altman plot and score plot based on principal component analysis (PCA) were used for visual comparison.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...