Efficient and productive asymmetric Michael addition: development of a highly enantioselective quinidine-based organocatalyst for homogeneous recycling via nanofiltration
Abstract
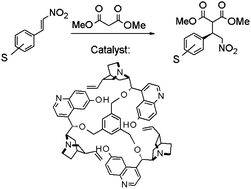
The relatively high cost and low availability of chiral organocatalysts, in addition to the high catalytic loading required (typically 1–30 mol%), pose a general challenge to the industrial development of economical asymmetric organocatalytic processes. This challenge can be addressed by recycling the organocatalysts. In this work, the potential of a class of organocatalysts, based on the cinchona alkaloid quinidine, was evaluated for the enantioselective synthesis step of an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). Enlarging the organocatalysts through polyalkylation made the organocatalysts easier to recycle with organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN) membranes. Each organocatalyst candidate's molecular size, molecular charge and ability to form hydrogen bonds were all important factors which determined the membrane retention of the catalyst. The consideration of these three factors enabled the eventual identification of a catalyst, of MW = 1044 Da, that was almost completely retained by the membrane, making it well-suited for recycling via OSN. In addition, a marked improvement in catalytic performance was observed for the enlarged catalyst compared to the non-enlarged catalyst, with high enantioselectivities of >92% ee obtained for all catalysed asymmetric Michael additions. Finally, a 2-stage membrane process was implemented to improve the productivity of the catalyst recycling process, resulting in a 96% reduction of solvent required for the recycling process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...