Dendritic CdS assemblies for removal of organic dye molecules†
Abstract
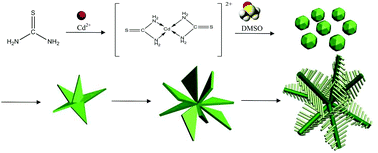
In this paper, novel CdS 3D assemblies are prepared via a facile and effective hydrothermal route using dimethyl sulfoxide as the growth template. Morphologies, microstructures and photocatalytic properties of the as-synthesized products are investigated in detail. It was found that dimethyl sulfoxide played an important role in the formation of CdS assemblies. A possible growth mechanism for CdS assemblies was proposed based on the experimental results. In addition, CdS assemblies exhibit superior photocatalytic activities by the photodegradation of eosin B, Methyl orange (MO) and Rhodamine B (RhB) under visible light irradiation, with a comparison with other CdS nanostructures, P25 and α-Fe2O3 powders, demonstrating potential applications in removal of organic dye molecules from waste water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...