pH and amine-induced various octamolybdate-based metal–organic complexes: assembly, structures and properties†
Abstract
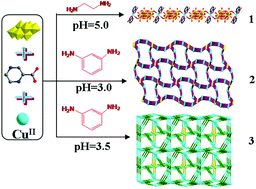
Three octamolybdate-based metal–organic complexes (MOCs), namely, [H2en]2[Cu(pzca)2(Mo8O26)]·4H2O (1), [Cu2(pzca)2(Mo8O26)0.5(H2O)4]·H2O (2) and [CuI3CuII4(pzca)7(Mo8O26)(H2O)2]·4H2O (3) (en = ethylenediamine, pzca = 2-pyrazinecarboxylic acid), have been successfully synthesized under hydrothermal conditions via adding different kinds of amine and adjusting the pH values. The single crystal X-ray diffraction, elemental analyses, IR spectra, and thermogravimetric analyses have been used to characterize the title complexes. In compound 1, the [Cu(pzca)2] units bridge the [β-Mo8O26]4− clusters to generate a 1D chain, which is extended by hydrogen-bonding interactions to a 3D supramolecular structure. Compound 2 exhibits a 3D coordination framework based on the 1D infinite [Cu2(pzca)2]n2n+ zigzag chains and β-Mo8O264− anions, and shows a trinodal 3,3,4-connected {83}4{86} topology containing a dodecagonal channel with the dimension of 13.496 × 19.642 Å2. Compound 3 is a 3D metal–organic network derived from the “λ”-like [Cu5(pzca)4] subunits and [β-Mo8O26]4− anions, which represents a novel {4·6·83·10}2{4·6·8}2{42·104}{42·83·10}{6·82}2{62·103·12}{62·82·102}{62·83·10}{63}4 topology in octamolybdate-based MOCs. The structural diversities show that the different amines and pH value of the reaction system play key roles in the construction of high dimensional architectures. Moreover, the electrochemical behaviors and photocatalytic activity for compound 1 have been investigated in detail.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...