Synthesis, structural characterization, and multichannel anion and cation sensing studies of a bifunctional Ru(ii) polypyridyl–imidazole based receptor†
Abstract
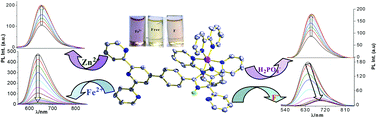
A mixed-ligand monometallic ruthenium(II) complex of composition [(bipy)2Ru(tpy-Hbzim-dipy)](ClO4)2 (1), where tpy-Hbzim-dipy = 4′-[4-(4,5-di-pyridin-2-yl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-phenyl]-[2,2′;6′,2′′]terpyridine and bipy = 2,2′-bipyridine has been synthesized and characterized using standard analytical and spectroscopic techniques including X-ray crystallography. The complex displays very intense, ligand centered absorption bands in the UV and moderately intense MLCT bands in the visible region. On excitation at the MLCT bands, the complex exhibits strong luminescence at room temperature with lifetimes in the range of 116–257 ns, depending upon the nature of the solvents. The complex is found to undergo one reversible oxidation in the positive potential window (0 to +1.8 V) and two successive quasi-reversible reductions in the negative potential window (0 to −2.0 V). Both anion and cation binding properties of the receptor were thoroughly investigated in acetonitrile solution using 1H NMR, absorption, steady state and time-resolved emission spectral studies and by cyclic voltammetry. The anion sensing studies revealed that the receptor acts as a “turn on” luminescence sensor for H2PO4− and HSO4− ions, and as a “turn off” sensor for F− and AcO− ions. It is evident that in the presence of excess F− and AcO− ions, deprotonation of the imidazole N–H fragment of the receptor occurs, an event which is signaled by the change of color from orange yellow to red visible to the naked eye. On the other hand, the probable mode of interaction of the receptors with H2PO4− and HSO4− ions is through hydrogen bonding interaction. The cation-sensing properties showed that the receptor was found to exhibit a colorimetric sensing ability that was highly selective for Fe2+, as evidenced by the distinct color change from yellow orange to deep red-violet to the naked eye over the other cations studied (Mn2+, Fe3+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...