New tris-3,4-HOPO lanthanide complexes as potential imaging probes: complex stability and magnetic properties†
Abstract
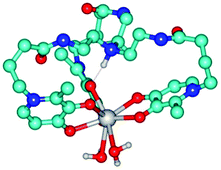
There is a growing interest in the development of new medical diagnostic tools with higher sensibility and less damage for the patient body, namely on imaging reporters for the management of diseases and optimization of treatment strategies. This article examines the properties of a new class of lanthanide complexes with a tripodal tris-3-hydroxy-4-pyridinone (tris-3,4-HOPO) ligand – NTP(PrHP)3. Among the studies herein performed, major relevance is given to the thermodynamic stability of the complexes with a series of Ln3+ ions (Ln = La, Pr, Gd, Er, Lu) and to the magnetic relaxation properties of the Gd3+ complex. This hexadentate ligand enables the formation of (1 : 1) Ln3+ complexes with high thermodynamic stability following the usual trend, while the Gd-chelates show improved relaxivity (higher hydration number), as compared with the commercially available Gd-based contrast agents (CAs); transmetallation of the Gd3+–L complex with Zn2+ proved to be thermodynamically and kinetically disfavored. Therefore, NTP(PrHP)3 emerges as part of a recently proposed new generation of CAs with prospective imaging sensibility gains.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemistry and applications of metal complexes

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...