Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene to styrene over alumina: effect of calcination
Abstract
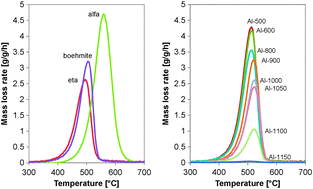
Commercially available γ-Al2O3 was calcined at temperatures between 500 and 1200 °C and tested for its performance in the oxidative ethylbenzene dehydrogenation (ODH) over a wide range of industrially-relevant conditions. The original γ-Al2O3, as well as η- and α-Al2O3, were tested. A calcination temperature around 1000/1050 °C turned out to be optimal for the ODH performance. Upon calcination the number of acid sites (from 637 to 436 μmol g−1) and surface area (from 272 to 119 m2 g−1) decrease, whereas the acid site density increases (from 1.4 to 2.4 sites per nm2). Less coke, being the active catalyst, is formed during ODH on the Al-1000 sample compared to γ-Al2O3 (30.8 wt% vs. 21.6 wt%), but the coke surface coverage increases. Compared with γ-Al2O3, the EB conversion increased from 36% to 42% and the ST selectivity increased from 83% to 87%. For an optimal ST selectivity the catalyst should contain enough coke to attain full conversion of the limiting reactant oxygen. The reactivity of the coke is changed due to the higher density and strength of the Lewis acid sites that are formed by the high temperature calcination. The Al-1000 sample and all other investigated catalysts lost ODH activity with time on stream. The loss of selectivity towards more COX formation is directly correlated with the amount of coke.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...