Absolute density measurement of SD radicals in a supersonic jet at the quantum-noise-limit†
Abstract
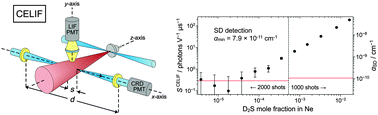
The absolute density of SD radicals in a supersonic jet has been measured down to (1.1 ± 0.1) × 105 cm−3 in a modestly specified apparatus that uses a cross-correlated combination of cavity ring-down and laser-induced fluorescence detection. Such a density corresponds to 215 ± 21 molecules in the probe volume at any given time. The minimum detectable absorption coefficient was quantum-noise-limited and measured to be (7.9 ± 0.6) × 10−11 cm−1, in 200 s of acquisition time, corresponding to a noise-equivalent absorption sensitivity for the apparatus of (1.6 ± 0.1) × 10−9 cm−1 Hz−1/2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...