Cationically rendered biopolymer surfaces for high protein affinity support matrices†
Abstract
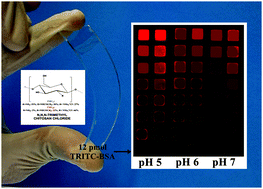
The use of cationic biopolymer surfaces for high protein binding affinity matrices is described. As model proteins, fluorescently labeled bovine serum albumins (FITC-BSA, TRITC-BSA) have been employed. The amount of proteins on such cationically rendered surfaces was quantified by QCM-D. In addition, flexible, transparent, patterned COP slides have been prepared and loaded with proteins ranging from 15 pM to 15 μM TRITC-BSA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...