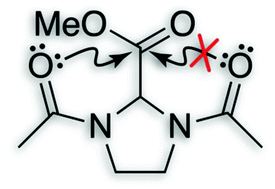
An n→π* interaction reduces the electrophilicity of the acceptor carbonyl group†
Abstract
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O⋯C′
O⋯C′![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O′) interactions are ubiquitous in both small and large molecular systems. This interaction involves delocalization of a lone pair (n) of a donor oxygen into the antibonding orbital (π*) of an acceptor carbonyl group. Analyses of high-resolution protein structures suggest that these
O′) interactions are ubiquitous in both small and large molecular systems. This interaction involves delocalization of a lone pair (n) of a donor oxygen into the antibonding orbital (π*) of an acceptor carbonyl group. Analyses of high-resolution protein structures suggest that these ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O′) to engage in more than one n→π* electron delocalization is probed using
O′) to engage in more than one n→π* electron delocalization is probed using

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...