Directed evolution of a synthetic RNA–protein module to create a new translational switch†
Abstract
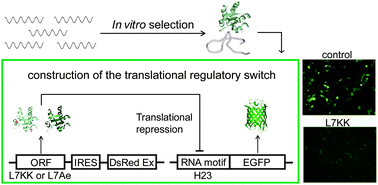
A synthetic RNP-binding module was developed to produce an alternative translational switch: an in vitro selection experiment targeting a derivative of L7Ae

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...