Energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry combined with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for simultaneous determination of zinc and copper in water samples
Abstract
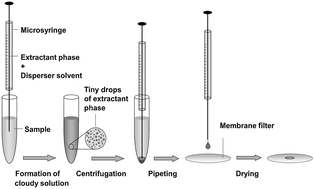
A dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction technique was successfully used as a sample preparation method for determination of trace amounts of zinc and copper ions in surface water by energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (EDXRF). The extraction method is based on the formation of sparingly soluble in water complexes of Zn and Cu with 2-(5-bromo-2-pyridylazo)-5-diethylamino-phenol (5-Br-PADAP). Some effective parameters of extraction and complex formation, such as extraction and disperser solvent type and their volume, pH, concentration of the chelating agent, and salt effect, have been optimized. Under the optimum conditions, the enrichment factor 250 was obtained from only 5 mL of a water sample. The calibration graph was linear from 0.02 to 0.4 μg mL−1 with detection limits of 1.8 ng mL−1 and 1.7 ng mL−1 for copper and zinc, respectively. The total RSD values for the EDXRF determination of Cu and Zn ions were 6.7% and 6.9%. Taking into account all steps preceding the determination and the uncertainty of EDXRF, the proposed method can be recognized as precise. The accuracy and repeatability of the proposed procedure were checked by the standard addition method and compared to the results obtained using the ICP-OES technique. The recovery in the range 91–95% was satisfactory and indicated the usefulness of the developed procedure.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...