An improved surface modification of poly(dimethylsiloxane) via a green chemistry approach for on-chip biomolecular separation
Abstract
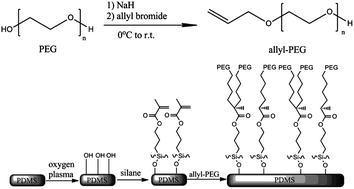
An enhanced facile strategy using a green chemistry method for the surface modification of poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) was developed via an in situ bulk free radical polymerization to resist nonspecific protein adsorption and to reduce electroosmotic flow (EOF). After silanization by 3-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane, allyl-polyethylene glycol (PEG) was conjugated onto the PDMS surface with the aid of sodium persulfate. The surface properties of PDMS were characterized with Fourier transform infrared absorption by attenuated total reflection (ATR-FTIR) and contact angle experiments. EOF measurements and a nonspecific protein adsorption assay revealed a stable EOF suppression and remarkable protein-repelling properties for more than 30 days. Separation of FITC-labeled amino acids demonstrated a high reproducibility (migration time, RSD 2.2%). Further separation of fluorescence-labeled proteins using PDMS microchips before and after the surface modification showed that the PEG-modified PDMS microchip had an improved electrophoretic performance with a RSD of 1.49% for the migration time. In summary, a convenient strategy was developed for the modification of a PDMS microchip to prevent nonspecific protein adsorption and to enhance the electrophoretic performance. This improved environmentally friendly surface modification method will be useful for protein separation especially in batch production.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...